Russia's mRNA Breakthrough: A Game Changer in the Fight against Cancer
Cancer is among the greatest concerns of the global population. According to the World Cancer Research Fund, a total of 19,976,499 cases of cancer were diagnosed in 2022. The age-standardized rate for all cancers for men and women combined was 196.9 per 100,000. The rate was higher for men (212.6 per 100,000) than women (186.3 per 100,000). Russia ranks fifth in the global cancer incidence in both sexes (including non-melanoma skin cancer). According to the Global Cancer Observatory, the total number of new cancer cases reported by the Russian Federation, in 2022, was 635,560. Of these, 301,496 cases were reported in males, and 334,064 cases were reported in females. The top three leading cancers (ranked by cases) include lung, prostate, colorectum, and breast, colorectum, and corpus uteri respectively.
Incidence and Mortality by Gender for the Top 15 Cancers**
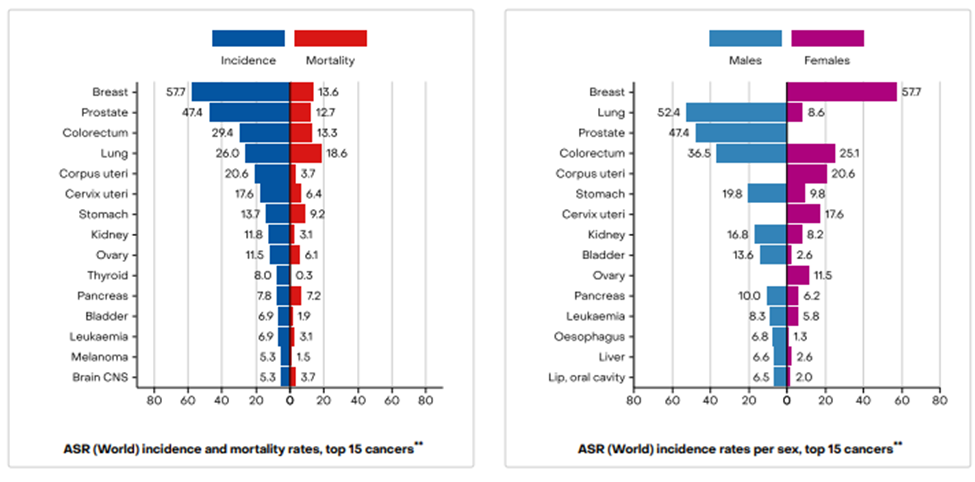
Source: Global Cancer Observatory
Note: ** NMSC included in other cancers
Additionally, the total cancer-related mortality in the region was 311,729. A total of 164,172 males and 147,557 females lost their lives to the disease during the period. The top three leading cancers (ranked by mortalities) include lung, colorectum, stomach, and breast, colorectum, and stomach respectively. Furthermore, the country has 1,868,265 number of prevalent cases of cancer (5-year period). The cases have been prevalent in 809,560 males, and 1 058,705 females.
Top 5 most frequent cancers**
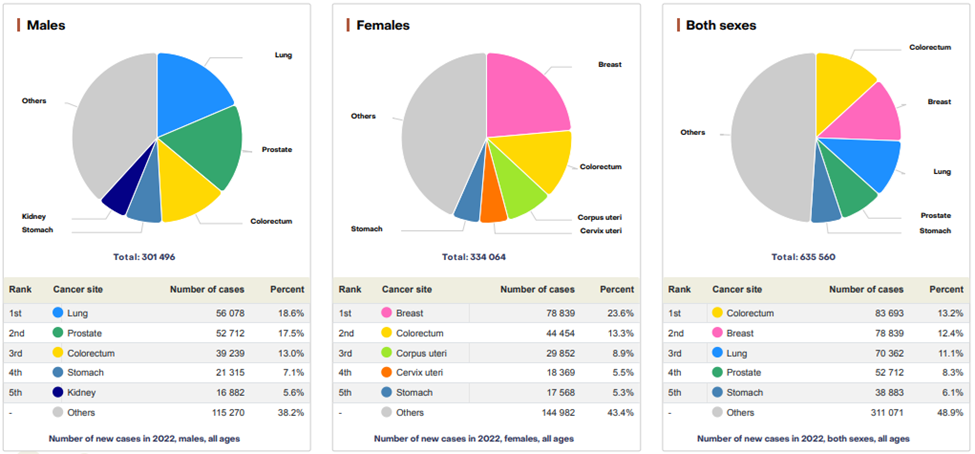
Source: Global Cancer Observatory
Note: ** NMSC included in other cancers
The burden of cancer is rising in almost every country, the prevention of which is a significant public health challenge. Around 40% of cancer cases could be prevented by tackling risk factors including diet, nutrition, and physical activity.
Russia is actively planning to do away with the situation. In order to build self-sufficiency to combat the growing incidence of cancer and bring down the cases of associated mortality, the country has developed an mRNA (messenger Ribonucleic Acid) vaccine. The vaccine will be distributed to patients for free and will be made available to the public by 2025. The vaccine will cost the Russian government 300,000 rubles ($3,594) per dose. It has been developed in partnership with several research centers.
During the pre-clinical trials, the vaccine was shown to suppress tumor development and potential metastases. The mRNA vaccine uses a small fragment of messenger RNA to produce a specific protein associated with cancer cells. The protein triggers the immune system to recognize and attack the cancer cells, effectively targeting the disease. Unlike traditional vaccines which use weakened or inactivated pathogens, mRNA vaccines leverage the body cells of the patients to create an immune response to treat cancer.
mRNA vaccines offer various advantages over conventional cancer vaccines, such as efficient production of protective immune responses, relatively low side effects, and lower cost of acquisition. The development of RNA-based vaccines is relatively faster and more inexpensive, owing to the high yields of In Vitro Transcription (IVT) reactions, and the recent advancements in industrial setups. However, conventional technologies, such as the incorporation of modified nucleosides, optimization of coding sequences, intranodal delivery of mRNA, ex vivo?loaded DCs, gene guns, and electroporation are complicated or expensive or too hard to be used in humans. Thus, the sector depicts opportunities for the development of innovative technologies to efficiently produce the mRNA vaccine. The recent innovations in mRNA technology include modification of mRNA structural elements, optimization of mRNA manufacturing platform, and development of mRNA delivery system. For instance, the adoption of a co?transcriptional coping strategy during IVT reaction reduces the cost of mRNA production. Similarly, compared to the Ion?Pair Reverse?Phase Chromatography (IPC) method, Ion?Exchange Chromatography (IEC) is more scalable and cost?effective, as it exhibits higher binding abilities.
The major players in the global cancer vaccine market include Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck & Co. Inc., GlaxoSmithKline plc, Eli Lilly and Company, Pfizer Inc., Dendreon Pharmaceuticals LLC, and Janssen Global Services, LLC, among others. The market players are contributing significantly to the market growth by the adoption of various business strategies, such as product development, mergers and acquisitions, partnerships, R&D, and more. For instance, in November 2023, Bristol Myers Squibb announced the initiation of translational medicine research in cancer biology. This includes research associated with gene expression in mRNA and miRNA.
In addition to the market players various global institutions are increasingly adopting mRNA vaccines for cancer treatment. For instance, in December 2023, the Oxford University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust (OUH), launched a new mRNA cancer vaccine trial for patients with head and neck cancer.
Moreover, in July 2024, the Albanese Government awarded more than $19 million to six research projects that use mRNA to prevent cancer and urinary tract infections. A team from the University of Queensland will receive $3.3 million to create a facility in Brisbane to design, make, and deliver mRNA vaccines for the treatment of cancer.
In a nutshell, the mRNA vaccine is stipulated to transform the cancer response landscape for Russia. The government is committed to fighting the rising incidence of the disease and plans to provide it to patients free of cost from 2025. The vaccine brings forth a novel method to target the cancerous cells, leveraging the patient's immune system, thus, increasing the chances of success of the therapy. As claimed by President Vladimir Putin, mRNA is truly the cancer vaccine and immunomodulatory drug of a new generation. Furthermore, as mRNA technology expands governments and research institutions globally are focusing on its large-scale adoption. The market players are expanding comprehensive research for the same, to ensure scalable and cost-effective production of cancer therapies. The shift is essential to ensure competence in the global cancer vaccine market.